Schedule Your Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
What is a Flare-up in Medical Terms?
A *flare-up* refers to an acute exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory condition, typically characterized by increased severity and duration of symptoms.
In medical terminology, a flare-up is often used to describe a sudden increase in the activity of a disease process, resulting in worsening symptoms and potentially affecting quality of life.
Flare-ups are commonly observed in conditions such as *inflammatory bowel disease* (e.g., *Crohn’s disease* and *ulcerative colitis*) and *rheumatological disorders* (e.g., *psoriatic arthritis* and *ankylosing spondylitis*).
In these conditions, the immune system becomes overly active, leading to inflammation and damage to tissues. A flare-up represents a sudden increase in this inflammatory activity, which can be triggered by various factors such as stress, certain foods, or infections.
During a flare-up, patients may experience increased frequency and severity of symptoms, including pain, *fatigue*, and *weight loss*. In some cases, a flare-up can be severe enough to require hospitalization and medical intervention.
The term *flare-up* is also used in the context of *asthma*, where it describes a sudden increase in airflow obstruction, often triggered by allergens or irritants.
In this sense, a flare-up can be treated with medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids, which aim to reduce inflammation and restore normal lung function.
Understanding the concept of a flare-up is crucial for effective management of chronic inflammatory conditions. By recognizing the triggers and warning signs of a flare-up, patients and healthcare providers can take proactive steps to prevent or mitigate its severity.
In addition, identifying the underlying causes of a flare-up is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. This may involve working with a healthcare provider to adjust medications, make lifestyle changes, or explore alternative therapies.
By taking a comprehensive approach to managing flare-ups, individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions can reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and maintain optimal health outcomes.
A flare-up in medical terms refers to a sudden and significant increase or worsening of symptoms associated with a chronic condition.
This phenomenon can manifest as an escalation of physical symptoms, such as pain, inflammation, or fatigue, which can disrupt daily life and overall well-being.
In the context of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), lupus, and multiple sclerosis, flares-ups are a common occurrence, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs.
During an RA flare-up, patients may experience increased joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, as well as morning stiffness that lasts for hours.
In the case of asthma, a flare-up can manifest as acute symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
Other chronic conditions that may experience flares-ups include inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriasis, and fibromyalgia.
The causes of flares-ups are multifaceted and can be triggered by various factors, including:
Environmental stressors: Hormonal changes, temperature extremes, humidity, and exposure to allergens or irritants can trigger a flare-up.
Medication interactions: Changes in medication regimens or dosages can lead to an over- or under-response of symptoms.
Hormonal fluctuations: Hormonal shifts during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can exacerbate chronic conditions and lead to flares-ups.
Emotional stress: Prolonged periods of emotional turmoil, anxiety, or depression can weaken the immune system and contribute to flares-ups.
Sleep disorders: Poor sleep quality, insomnia, or restless leg syndrome can exacerbate chronic conditions and worsen symptoms during flares-ups.
Early recognition and management are crucial for mitigating the impact of a flare-up, as they can help alleviate symptoms, reduce disease activity, and improve overall quality of life.
Working closely with a healthcare provider, patients can develop personalized strategies to manage their chronic conditions and minimize the risk of flares-ups.
By understanding the complexities of chronic diseases and the triggers that contribute to flares-ups, individuals and healthcare providers can develop targeted approaches for preventing and managing these episodes.
Regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and medication adjustments can help reduce the frequency and severity of flares-ups, allowing patients to better navigate their chronic conditions and enjoy improved overall well-being.
Causes and Triggers of Flare-ups
A flaring, also known as a flare-up or exacerbation, is a sudden increase in symptoms or severity of a chronic condition. In medical terms, it refers to a rebound worsening of an underlying disease process, resulting in increased inflammation, pain, or disability.
The causes and triggers of flares are multifaceted and can vary depending on the specific condition being affected. However, some common culprits include:
Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger a flare-up by causing the body to release stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can exacerbate inflammation and worsen symptoms.
Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as cold temperatures, humidity changes, or exposure to allergens, can also trigger flares in people with chronic conditions.
Medication Interactions: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and NSAIDs, can actually trigger flares by suppressing the immune system or altering hormone levels, leading to a rebound effect when taken at low doses for extended periods.
Sleep Disturbances: Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt the body’s natural inflammatory response and increase inflammation, making it more susceptible to flares.
Dietary Factors: Consuming trigger foods or skipping essential nutrients can also contribute to flares in people with chronic conditions. For example, a low-fiber diet can worsen symptoms in people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Overexertion: Engaging in physical activity that is too strenuous or prolonged can lead to muscle strain and exacerbate existing conditions.
Underlying Conditions: The presence of underlying medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal disorders, autoimmune diseases, or respiratory conditions, can also trigger flares by creating an inflammatory response.
Lack of Exercise: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to inflammation and worsen symptoms in people with chronic conditions, while regular exercise has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Poor Posture or Biomechanics: Abnormal posture or biomechanical alignment can put additional strain on muscles and joints, leading to increased inflammation and discomfort.
Emotional Factors: Mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and stress can also contribute to flares in people with chronic conditions by altering the body’s response to pain and stress.
Other Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or vitamin deficiencies, can also trigger flares by disrupting normal bodily functions.
Consult with Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers Now
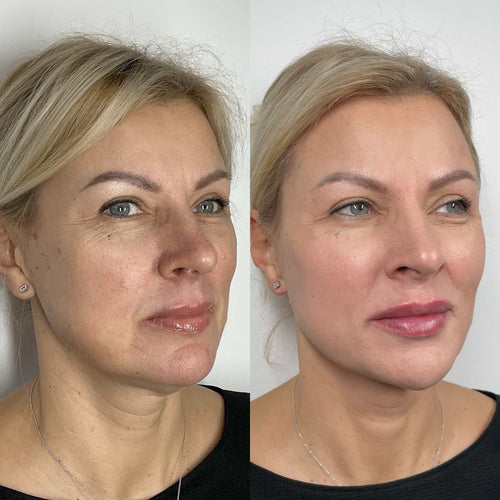

Family History: A family history of chronic conditions can increase the risk of developing similar conditions and experiencing flares.
Age-Related Changes: As we age, our bodies undergo natural changes that can affect inflammation levels, making us more susceptible to flares in certain conditions.
Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors can contribute to an individual’s risk of developing chronic conditions and experiencing flares, particularly if there is a family history of similar conditions.
Anti-inflammatory Medications: Some medications used to treat conditions such as asthma or rheumatoid arthritis can actually trigger flares by altering normal inflammatory processes.
A flare-up in medical terms refers to an acute increase in symptoms, severity, and frequency of a chronic condition, often accompanied by inflammation and tissue damage.
In conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), or lupus, stress and emotional turmoil can trigger flare-ups. These triggers can be complex and multi-factorial, involving psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and changes in sleep patterns, as well as physiological responses to perceived threats.
Stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline are released in response to perceived threats or challenges, which can exacerbate inflammation and worsen symptoms. Additionally, chronic stress can also suppress the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to regulate its own inflammatory response.
Other factors that can trigger flare-ups in conditions like RA and lupus include cold weather, changes in barometric pressure, and hormonal fluctuations. In contrast, asthma patients may experience exacerbations triggered by factors such as air pollution, cold temperatures, allergens, and respiratory infections.
Air pollution is a significant trigger for asthma flare-ups, particularly in urban areas with high levels of particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Cold weather can also make asthma symptoms worse, possibly due to changes in lung function, airway resistance, and the release of inflammatory mediators.
Respiratory infections are another common trigger for asthma flare-ups. These infections can irritate the airways, increase mucus production, and promote inflammation. In people with underlying lung conditions like COPD or cystic fibrosis, respiratory infections can be particularly problematic.
Viral infections, including common colds and flu, can also exacerbate symptoms in asthma patients. This is because viral infections can cause inflammation, increase airway resistance, and lead to increased mucus production, making it more difficult to breathe.
Other factors that may contribute to flare-ups in asthma include allergies, smoking, and exposure to irritants like tobacco smoke and strong odors. Additionally, certain medications, such as beta blockers and corticosteroids, can also trigger or worsen asthma symptoms.
In contrast, cold weather is a well-known trigger for flare-ups in conditions like lupus and RA. Changes in barometric pressure may contribute to the development of symptoms, possibly by altering blood flow and kidney function. Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation or menopause can also exacerbate symptoms in some individuals with these conditions.
Other factors that may contribute to flare-ups in lupus include stress, sun exposure, and certain medications. Certain infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), have been associated with an increased risk of developing lupus in susceptible individuals.
It is essential to note that everyone’s triggers and patterns are unique, and it may take time and experimentation to identify the specific factors that contribute to flare-ups in your condition. Working closely with your healthcare provider can help you develop a personalized plan for managing symptoms and reducing the risk of flare-ups.
Identifying and Managing Flare-ups
Identifying and managing flare-ups are crucial steps in maintaining overall health, especially for individuals with chronic conditions. A flare-up refers to an episode or episode-like condition that intensifies symptoms, making it difficult for the individual to manage their daily life.
In medical terms, a flare-up is often characterized by an increase in inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and others. It may also be accompanied by worsening symptoms, which can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain.
The importance of prompt action during a flare-up cannot be overstated. Delaying treatment or neglecting early warning signs can lead to more severe complications, prolonged recovery periods, and even permanent damage to organs or tissues.
- Understanding the triggers: Identifying the causes of flare-ups is essential for developing an effective management plan. Common triggers include stress, infection, allergic reactions, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
- Monitoring symptoms: Paying attention to early warning signs, such as increased fatigue, joint pain, or digestive issues, can help individuals take proactive steps to mitigate the flare-up.
- Seeking medical attention: If a flare-up is severe, frequent, or persistent, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and support. They may prescribe medication, adjust treatment plans, or recommend lifestyle changes to prevent future episodes.
- Self-management techniques: Individuals can also employ various self-management strategies to reduce the severity of flare-ups, including:
- Stress management: Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help alleviate stress-related symptoms.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise, like walking or swimming, can improve mood and reduce inflammation.
- Dietary changes: Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in whole foods, fruits, and vegetables can help mitigate the effects of flare-ups.
Additionally, developing a comprehensive treatment plan that incorporates these elements can significantly improve the chances of successful flare-up management. By working collaboratively with healthcare professionals, individuals can create personalized strategies that address their unique needs and circumstances.
Prompt action during a flare-up is also essential for preventing long-term consequences, such as:
- Chronic disease progression: Delaying treatment or neglecting early warning signs can lead to the progression of underlying chronic conditions.
- Complications and comorbidities: Ignoring flare-ups can increase the risk of developing complications and comorbidities, such as cardiovascular disease, respiratory problems, or mental health disorders.
- Poor quality of life: Inadequate management of flare-ups can significantly impact an individual’s daily activities, social relationships, and overall well-being.
In conclusion, identifying and managing flare-ups is a critical aspect of maintaining good health. Prompt action, combined with effective self-management strategies and comprehensive treatment plans, can help prevent long-term consequences and improve the quality of life for individuals living with chronic conditions.
A flaring in medical terms refers to an increase in symptoms and inflammation in chronic conditions such as asthma, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and lupus. Understanding and managing flare-ups is crucial for patients to maintain control over their condition and prevent long-term damage.
In asthma, a flare-up occurs when the airways become inflamed and constricted, leading to difficulty breathing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Asthma sufferers need to be aware of early warning signs, such as:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Coughing or chest pain
Secure a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Asthma sufferers should also know how to manage their symptoms using medication, such as bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and combination inhalers. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as avoiding triggers like tobacco smoke, pollution, and stress can help prevent flare-ups.
In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a flare-up occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the body, leading to inflammation and pain in the joints. RA patients need to work closely with their healthcare providers to adjust medication regimens and make lifestyle changes to prevent future flare-ups.
- Medication adjustments: changing or adding medications to reduce inflammation and symptoms
- Lifestyle modifications: exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and stress management
- Therapy: physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy to maintain joint mobility and function
- Social support: connecting with others who have RA, joining support groups, and seeking emotional support
In lupus, a flare-up occurs when the immune system attacks healthy tissues in multiple organs, leading to inflammation and symptoms. Lupus patients need to work closely with their healthcare providers to adjust medication regimens and make lifestyle changes to prevent future flare-ups.
- Medication adjustments: changing or adding medications to reduce inflammation and symptoms
- Lifestyle modifications: maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and stress management
- Sun protection: avoiding excessive sun exposure and using sunscreen, clothing, and sunglasses for UV protection
- Self-care: engaging in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as meditation, yoga, or reading
Managing flare-ups requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and self-care strategies. By being aware of early warning signs and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can take proactive steps to prevent future flare-ups and maintain control over their condition.
Read more about Prince and Flower here. Read more about Tattoo Culture Magazine here. Read more about Fashionably Balanced here. Read more about Prince and Flower here. Read more about Highland Spring Magazine here. Read more about Back to Work Experts here.
- NCTF 135 HA Near West Molesey, Surrey - December 31, 2024
- How Often To Get Lip Filler - December 17, 2024
- What Is A Flaring In Medical Terms? - December 10, 2024